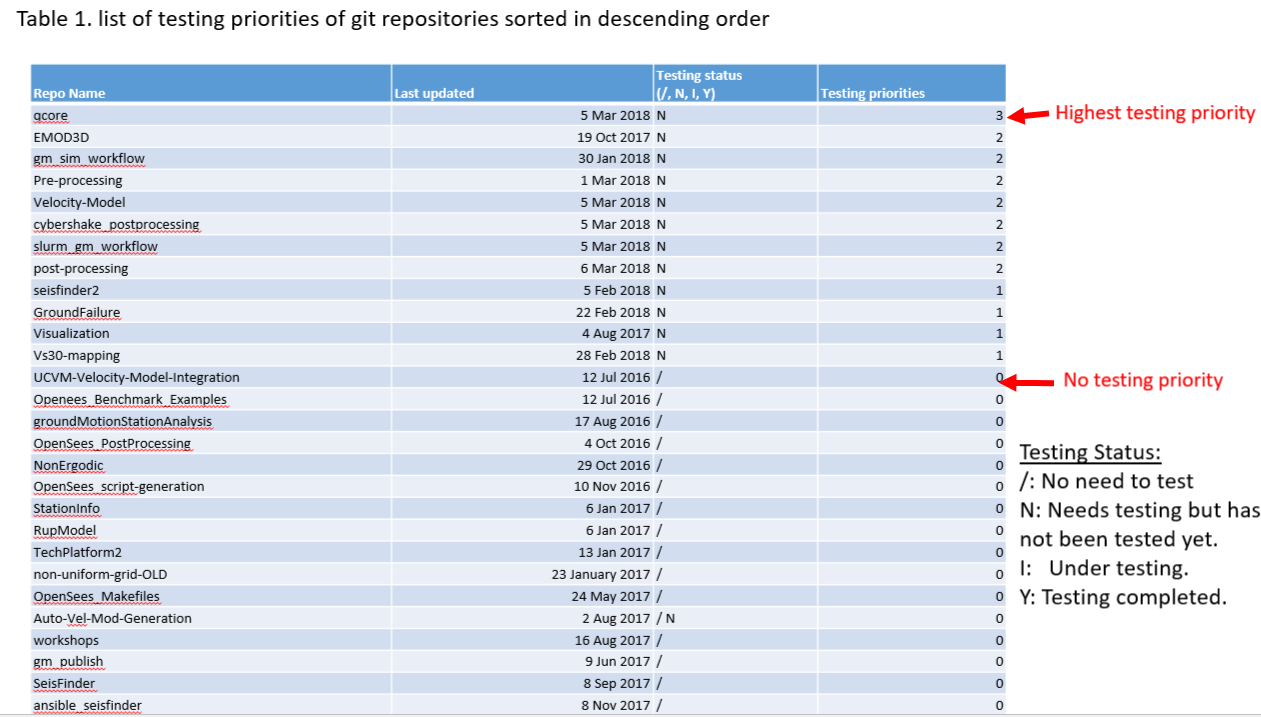
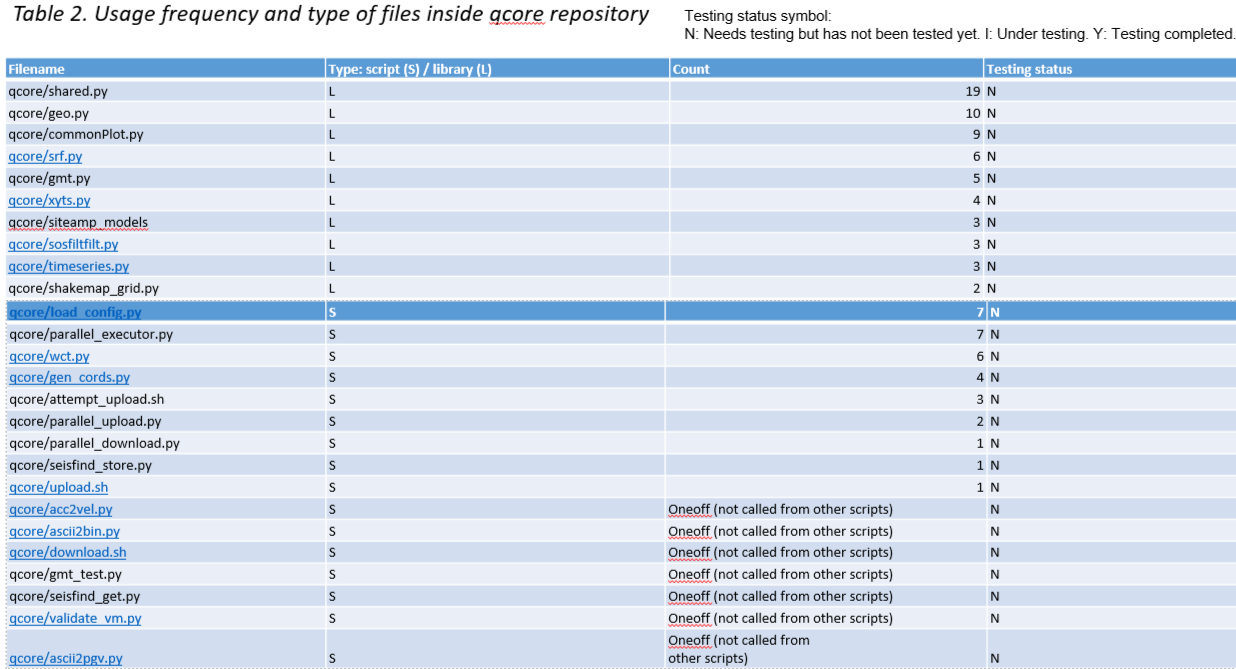
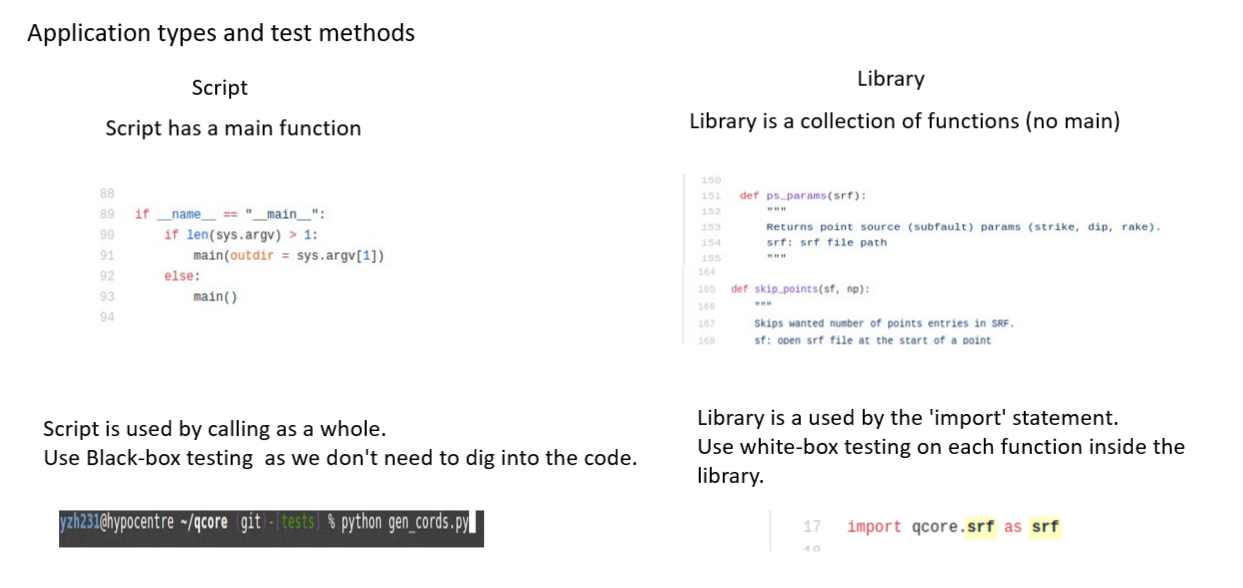
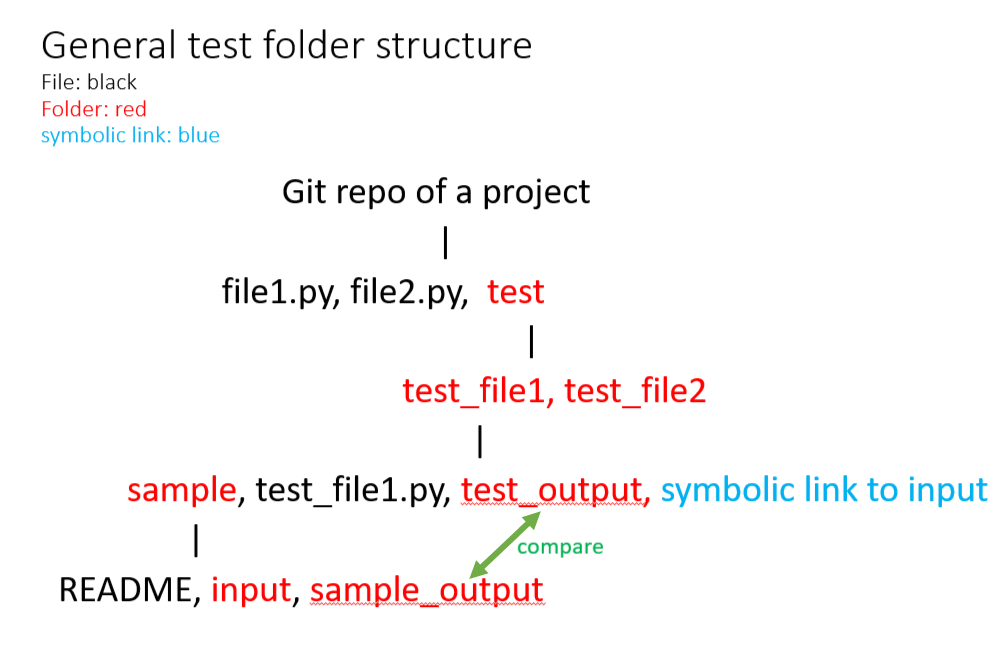
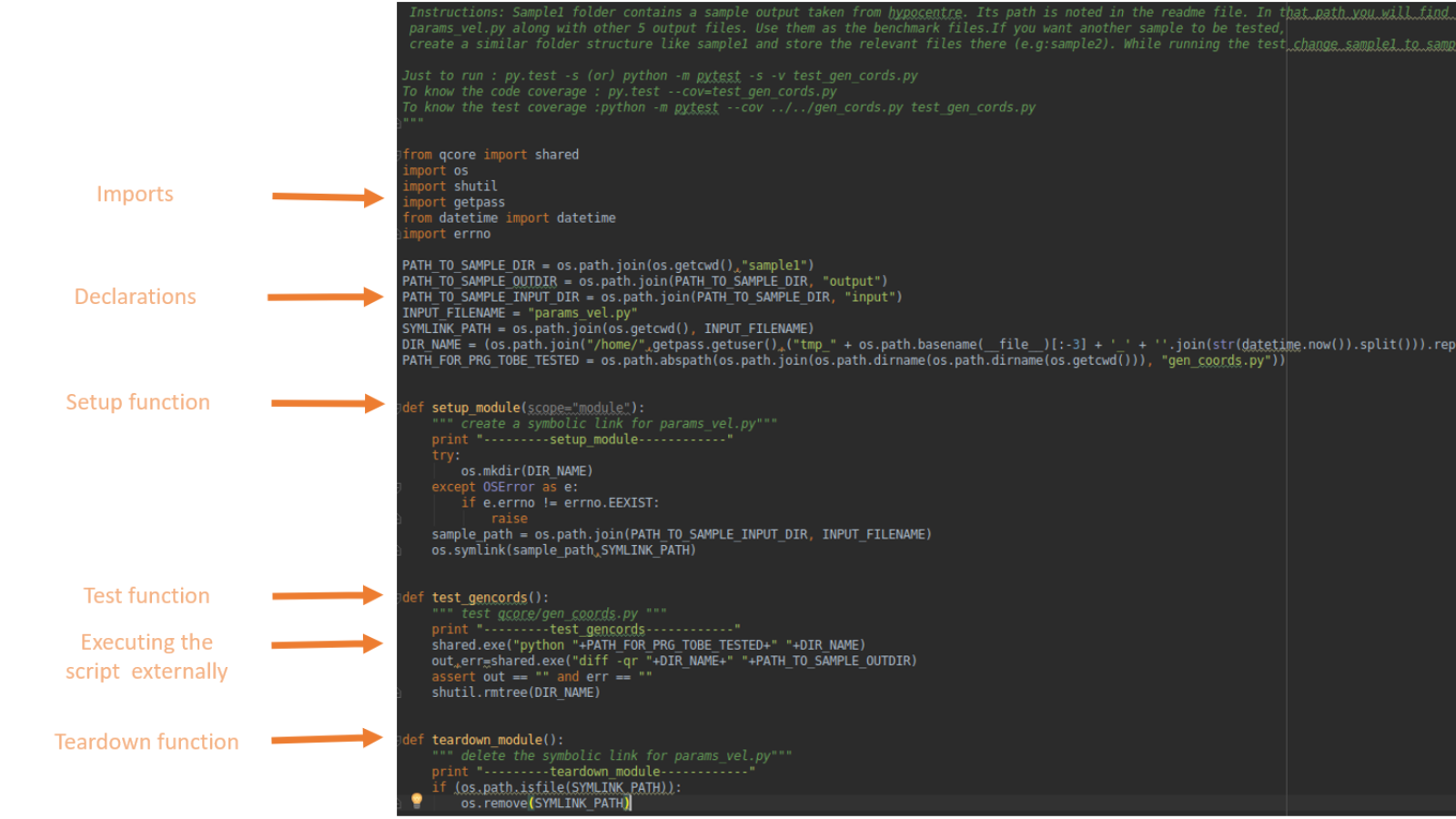
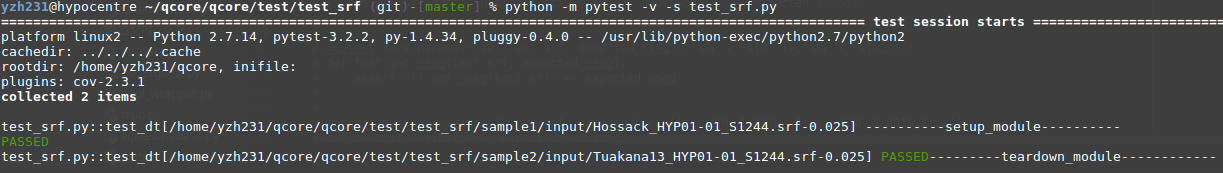
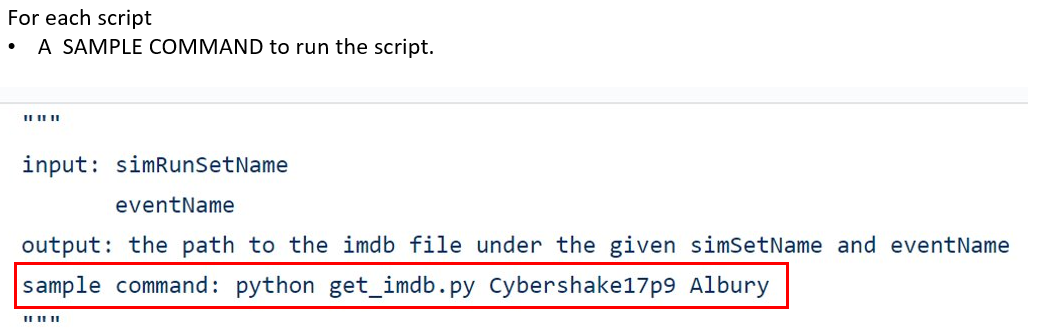
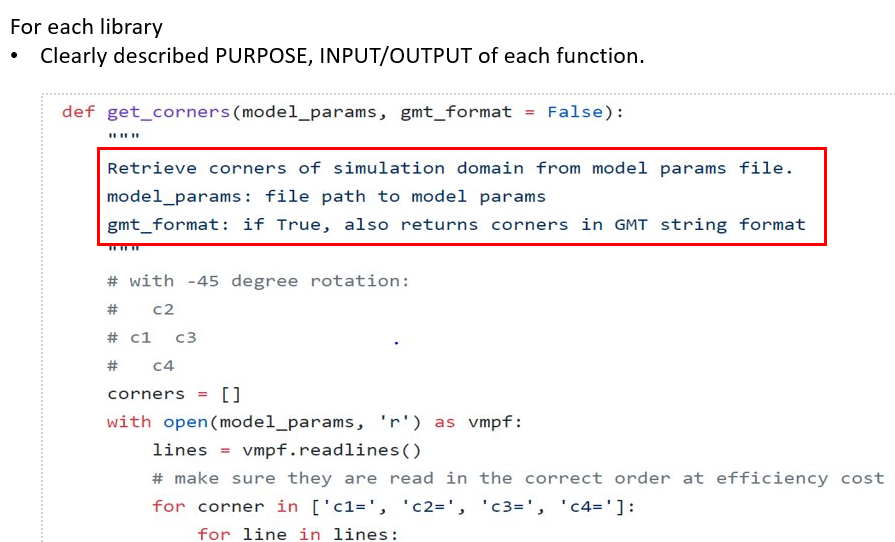
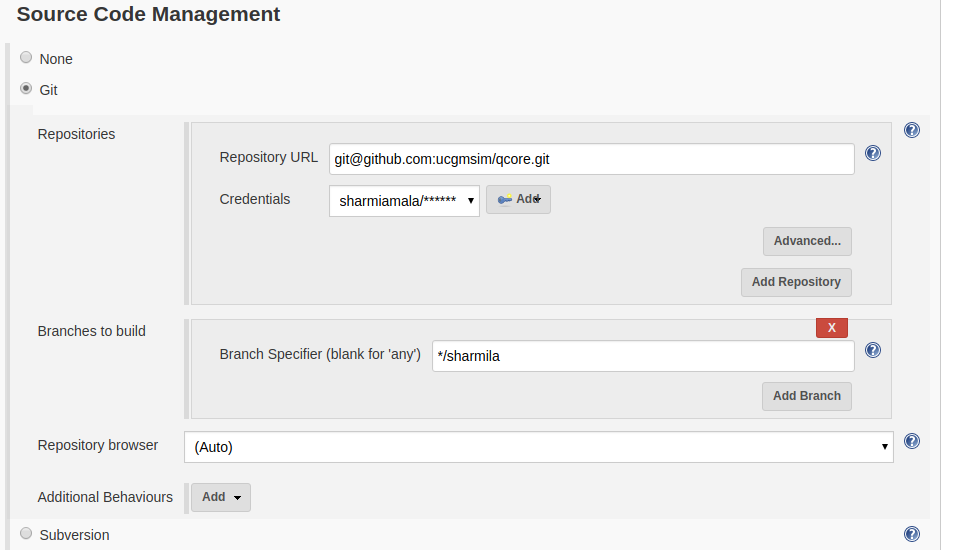
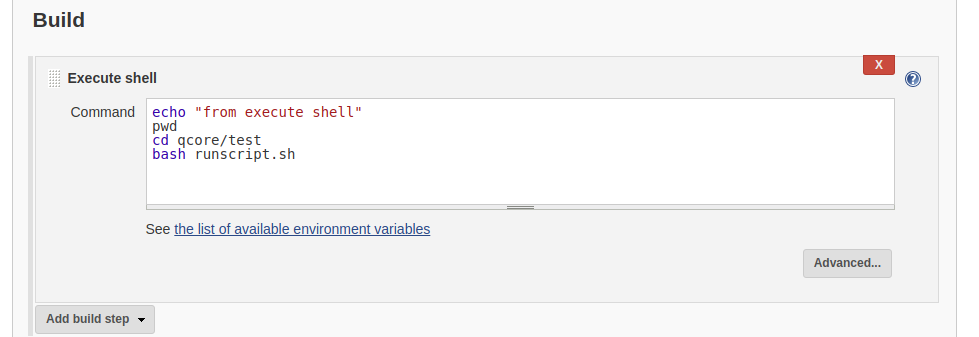
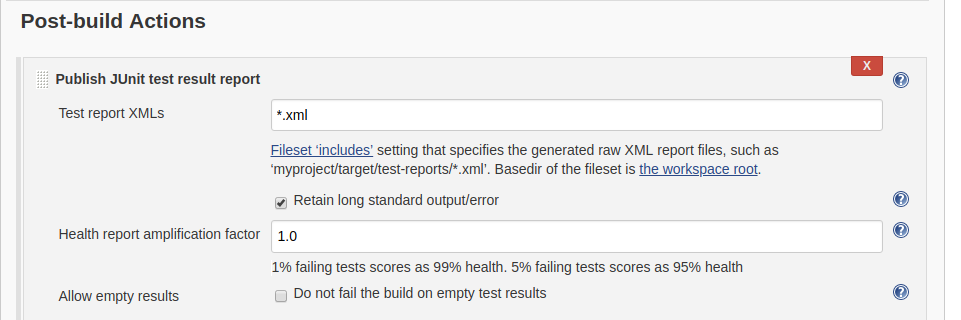
""" Command to run this test: 'python -m pytest -v -s test_srf.py'
To know the code coverage : py.test --cov=test_srf.py
To know the test coverage :python -m pytest --cov ../../srf.py test_srf.py
"""
from qcore import srf, shared
import pytest
from datetime import datetime
import os
import numpy as np
import sys
import getpass
import shutil
import errno
ERROR_LIMIT = 0.001
SRF_1_PATH = os.path.join(os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)), "sample1/input/Hossack_HYP01-01_S1244.srf")
SRF_2_PATH = os.path.join(os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)), "sample2/input/Tuakana13_HYP01-01_S1244.srf")
SRF_3_PATH = os.path.join(os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)), "sample3/input/single_point_source.srf")# This is a fake one, just created for testing single point source
SRF_1_CNR_PATH = os.path.join(os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)), "sample1/output/cnrs.txt")
SRF_2_CNR_PATH = os.path.join(os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)), "sample2/output/cnrs.txt")
SRF_1_OUT_ARRAY_SRF2LLV = os.path.join(os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)), "sample1/output/out_array_srf2llv.bin")
SRF_2_OUT_ARRAY_SRF2LLV = os.path.join(os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)), "sample2/output/out_array_srf2llv.bin")
SRF_1_OUT_ARRAY_SRF2LLV_PY = os.path.join(os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)), "sample1/output/out_array_srf2llv_py.bin")
SRF_2_OUT_ARRAY_SRF2LLV_PY = os.path.join(os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__)), "sample2/output/out_array_srf2llv_py.bin")
SRF_1_PLANES = srf.read_header(SRF_1_PATH, True)
SRF_2_PLANES = srf.read_header(SRF_2_PATH, True)
HEADERS = ['centre', 'nstrike', 'ndip', 'length', 'width', 'strike', 'dip', 'dtop', 'shyp', 'dhyp']
DIR_NAME = (os.path.join("/home/",getpass.getuser(),("tmp_" + os.path.basename(__file__)[:-3] + '_' + ''.join(str(datetime.now()).split())).replace('.', '_')).replace(':', '_'))
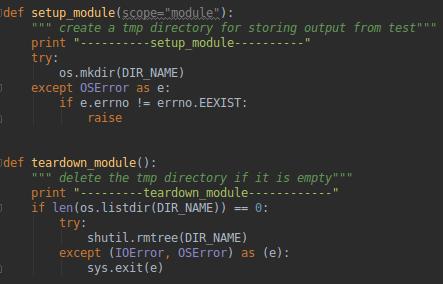
def setup_module(scope="module"):
""" create a tmp directory for storing output from test"""
print "----------setup_module----------"
try:
os.mkdir(DIR_NAME)
except OSError as e:
if e.errno != errno.EEXIST:
raise
def teardown_module():
""" delete the tmp directory if it is empty"""
print "---------teardown_module------------"
if len(os.listdir(DIR_NAME)) == 0:
try:
shutil.rmtree(DIR_NAME)
except (IOError, OSError) as (e):
sys.exit(e)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("plane, expected_values",[( SRF_1_PLANES[0], [[176.2354,-38.3404], 34, 92, 3.44, 9.24, 230, 60, 0.00, 0.00, 5.54]),
(SRF_2_PLANES[0],[[176.8003, -37.0990], 46, 104, 4.57, 10.44, 21, 50, 0.00, 0.00, 6.27]),
(SRF_2_PLANES[1], [[176.8263, -37.0622], 49, 104, 4.89, 10.44, 37, 50, 0.00, -999.90, -999.90])])
def test_plane(plane, expected_values):
""" Tests for the header lines """
for i in xrange(len(HEADERS)):
assert(plane[HEADERS[i]] == expected_values[i])
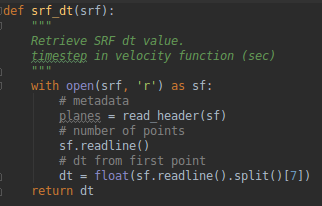
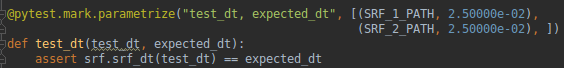
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_dt, expected_dt", [(SRF_1_PATH, 2.50000e-02),
(SRF_2_PATH, 2.50000e-02), ])
def test_dt(test_dt, expected_dt):
assert srf.srf_dt(test_dt) == expected_dt
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_dxy, expected_dxy",[(SRF_1_PATH, (0.10,0.10)),
(SRF_2_PATH,(0.1,0.10)),])
def test_dxy(test_dxy, expected_dxy):
assert srf.srf_dxy(test_dxy) == expected_dxy
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_srf,filename,sample_cnr_file_path",[(SRF_1_PATH,'cnrs1.txt',SRF_1_CNR_PATH), (SRF_2_PATH,'cnrs2.txt',SRF_2_CNR_PATH)])
def test_srf2corners(test_srf,filename,sample_cnr_file_path):
# NOTE : The testing was carried out based on the assumption that the hypocentre was correct
# srf.srf2corners method calls the get_hypo method inside it, which gives the hypocentre value
abs_filename = os.path.join(DIR_NAME,filename)
print "abs_filename: ",abs_filename
srf.srf2corners(test_srf,cnrs=abs_filename)
out, err = shared.exe("diff -qr " + sample_cnr_file_path + " " + abs_filename)
assert out == "" and err == ""
try:
os.remove(abs_filename)
except (IOError, OSError):
raise
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_srf,expected_latlondepth",[(SRF_1_PATH, {'lat': -38.3354, 'depth': 0.0431, 'lon': 176.2414}),\
(SRF_2_PATH, {'lat': -37.1105, 'depth': 0.0381, 'lon': 176.7958}
)])
def test_read_latlondepth(test_srf,expected_latlondepth): #give you so many lat,lon,depth points
points = srf.read_latlondepth(test_srf)
assert points[9] == expected_latlondepth # 10th point in the srf file
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_srf,seg,depth,expected_bounds",[(SRF_1_PATH, -1, True,[[(176.2493, -38.3301, 0.0431), (176.2202, -38.3495, 0.0431), (176.1814, -38.3221, 7.886), (176.2105, -38.3027, 7.886)]]
),(SRF_2_PATH, -1, True,[[(176.7922, -37.118, 0.0381), (176.8101, -37.0806, 0.0381), (176.876, -37.1089, 7.8931), (176.8581, -37.1464, 7.8931)], [(176.8107, -37.0798, 0.038), (176.8433, -37.0455, 0.038), (176.9092, -37.0739, 7.8672), (176.8765, -37.1082, 7.8672)]]), \
(SRF_1_PATH, -1, False,[[(176.2493, -38.3301), (176.2202, -38.3495), (176.1814, -38.3221), (176.2105, -38.3027)]]
),(SRF_2_PATH, -1, False,[[(176.7922, -37.118), (176.8101, -37.0806), (176.876, -37.1089), (176.8581, -37.1464)], [(176.8107, -37.0798), (176.8433, -37.0455), (176.9092, -37.0739), (176.8765, -37.1082)]]
)])
def test_get_bounds(test_srf, seg, depth, expected_bounds):
assert srf.get_bounds(test_srf, seg=seg, depth=depth) == expected_bounds
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_srf, expected_nseg",[(SRF_1_PATH, 1),(SRF_2_PATH,2)])
def test_get_nseg(test_srf, expected_nseg):
assert srf.get_nseg(test_srf) == expected_nseg
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_srf, expected_result",[(SRF_1_PATH, True),(SRF_2_PATH,True)])
def test_is_ff(test_srf, expected_result):
assert srf.is_ff(test_srf) == expected_result
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_srf_planes, expected_result",[(SRF_1_PLANES, 1),(SRF_2_PLANES,2)])
def test_nplane1(test_srf_planes, expected_result):
assert len(test_srf_planes) == expected_result
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_srf, expected_result",[(SRF_1_PATH,(AssertionError)),(SRF_2_PATH,AssertionError),(SRF_3_PATH,(0, 60, 30))])
def test_ps_params(test_srf, expected_result):
try:
srf.ps_params(test_srf)
print "point is single- in try block"
except AssertionError:
print "point is not single-except block "
return
assert srf.ps_params(test_srf) == expected_result #only check strike, dip, rake values if it is a single point source
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_srf, sample_out_array",[(SRF_1_PATH,SRF_1_OUT_ARRAY_SRF2LLV),(SRF_2_PATH,SRF_2_OUT_ARRAY_SRF2LLV)])
def test_srf2llv(test_srf, sample_out_array):
sample_array = np.fromfile(sample_out_array, dtype='3<f4')
out_array = srf.srf2llv(test_srf)
compare_np_array(sample_array,out_array,ERROR_LIMIT)
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_srf, sample_out_array",[(SRF_1_PATH,SRF_1_OUT_ARRAY_SRF2LLV_PY),(SRF_2_PATH,SRF_2_OUT_ARRAY_SRF2LLV_PY)],)
def test_srf2llv_py(test_srf, sample_out_array):
sample_array = np.fromfile(sample_out_array, dtype = '3<f4')
out_array_list = srf.srf2llv_py(test_srf)
print("Adsfafsaf",out_array_list)
out_array = out_array_list[0]
# out_array[0] += 1 # Use this, if you want to test for a fail case, by changing a value in the out_array
for array in out_array_list[1:]:
out_array = np.concatenate([out_array, array])
print("first out array", out_array)
compare_np_array(sample_array,out_array,ERROR_LIMIT)
def compare_np_array(array1, array2, error_limit):
"""array1: a numpy array from sample output, will be used as the denominator,
array2: a numpy array from test output, makes part of the numerator.
error_limit: preset error_limit to be compared with the relative error (array1-array2)/array1
"""
assert array1.shape == array2.shape
relative_error = np.divide((array1 - array2), array1)
print "relative_error: *********** ", relative_error
max_relative_error = np.nanmax(np.abs(relative_error))
print "max_relative_error: *********** ", max_relative_error
assert max_relative_error <= error_limit
|